Neobanks have rapidly transformed the financial landscape, driven by the growing demand for digital-first banking and continuous advances in fintech. As of 2025, there are nearly 317 neobanks worldwide, serving 400 million users. With no signal of slowing down, the global neobank market is predicted to reach USD 3,406.47 billion by 2032 at a CAGR of 48.6%, offering numerous opportunities for startups and businesses.
These branchless, digital-only banks cater to evolving customer needs such as personalization, instant payments, and niche business services. Nearly 30% of new accounts in 2024 were opened by small businesses, freelancers, or regulated sectors, highlighting strong market demand.
At the same time, founders and businesses exploring this sector should be aware of regulatory compliance, cybersecurity, and sustainable profitability, which remain critical challenges in scaling a neobank.
This article provides an overview of what neobanks are, how they operate, and the key trends shaping this fast-growing industry.
What is a neobank?
A neobank is a digital-only bank that operates entirely online with no physical branches. Everything runs through a mobile app or website, from opening an account to making transfers or tracking spending.
Some of the biggest names in this neobanking world include Revolut (UK), N26 (Germany), Chime (USA), NuBank (Brazil), Starling Bank (UK). They serve individuals and businesses with all-in-one financial apps, and offer features like smart budgeting tools, multi-currency accounts, seamless international payments, and cryptocurrency trading. With user-friendly interfaces, low or no fees, and real-time financial insights, they make banking more accessible, transparent, and convenient.
How do neobanks differ from traditional and digital banks?
Now that we know what neobanks are, you might be wondering: aren’t all banks going digital these days? What makes them truly different from traditional banks or digital banking services?
Here are the key differences:
Neobank vs. traditional banks
| Feature | Neobank | Traditional bank |
|---|---|---|
| Operational model | Entirely digital, no physical branches | Physical branches |
| Technology & innovation | Cloud, API, AI, automation, open banking | Legacy systems limited adopt new technologies |
| Cost structure | Lower operational costs and higher competitive of pricing and innovation | Higher overhead costs due to physical branches and infrastructure |
| Service offerings | Mainly digital banking solutions, such as fee-free transactions, budgeting tools, etc. | Various financial services such as loans, mortgages, investment advisory |
| Customer support | Primarily app-based with chatbots and digital assistance | In-person support along with digital services |
Neobank vs. digital banks
| Feature | Neobank | Digital bank |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership & regulation | Independent fintech companies with different regulatory requirements | Often subsidiaries of traditional banks, adhering to the same banking regulations |
| Service scope | Focuses on niche financial products | Combine traditional and modern banking services |
| Customer approach | Agile, innovation-driven, integrated fintech solutions | Balances innovation with regulatory and operational constraints of its parent bank |
| Banking license | Operates without a banking license, partnering with licensed banks instead | Holds a banking license under the parent bank’s regulation |
| Flexibility & innovation | More experimental and adaptable to market changes | Limited by the regulations and strategies of the parent bank |
These differences explain why neobanks have gained such rapid traction. They’re built to be fast, innovative, and user-friendly from the ground up.
But here’s the interesting part. How do they pull it all off without physical branches or legacy systems? The next part will explain it.
How do neobanks work?
These differences explain why neobanks have gained such rapid traction. They’re built to be fast, innovative, and user-friendly from the ground up.
But here’s the interesting part. How do they pull it all off without physical branches or legacy systems? The next part will explain it.
Main architectural models in neobanking
Depending on how much control a neobank wants to have over its infrastructure, there are four common architectural models:
| Model | Description | Example use case |
|---|---|---|
| Full-stack neobank | The neobank builds and owns its entire core banking system, payment rails, and regulatory license. | Varo Bank (US) |
| BaaS-based (Banking-as-a-Service) | The neobank relies on a licensed partner bank’s infrastructure via APIs for accounts, compliance, and payments. | Chime, Monese |
| API-first neobank | Focused on building a flexible API layer that connects the user interface (app, website) to third-party services (KYC, payments, lending, cards). | Revolut, Starling |
| Front-end / White-label model | Only the customer-facing layer (like the app and UX) is built internally, while the banking engine and core system are outsourced to backend vendors. | Niche / regional neobanks |
To put it simply:
Full-stack gives you the most control, but requires a lot of time, money, and regulatory work.
BaaS and API-first models enable quicker setup and lower regulatory burden.
Front-end / White-label model is the lightest to set up, but offers the least flexibility in backend operations.
No matter which architecture a neobank chooses, they all need the same essential system modules under the hood. Here’s what’s inside.
Common system modules inside a neobank
Account Management: Handles creating and maintaining customer accounts, and linking them to wallets or deposit facilities.
Ledger System: Records all transactions in real time, reconciles balances, and supports reporting.
Payments Engine: Manages transfers and rails for local and international payments (ACH, SEPA, real-time payments, etc.)
Card Issuing & Processing: Supports issuing, tokenizing, and sponsoring cards, and managing fraud risk.
KYC / AML Module: Verifies customer identities and monitors transactions to comply with regulations.
FX & Cross-Border Module: Supports multi-currency accounts, currency conversion, and cross-border payments.
Analytics & Reporting: Tracks user behavior, financial metrics, and regulatory reports for compliance and business insights.
These modules form the technical backbone of a neobank. While the models above decide how much infrastructure the neobank owns vs outsources, these building blocks remain consistent across most neobanks.
Collaboration and compliance
Most neobanks operate through partnerships rather than handling everything on their own. This is mainly because banking is a highly regulated industry, and working with licensed financial institutions helps neobanks launch faster while staying compliant.
Neobanks typically collaborate with:
- Licensed banks that provide account infrastructure, deposit protection, and access to payment networks.
- Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) providers that offer APIs for KYC, payments, card issuing, and regulatory reporting.
Through these partnerships, the neobank can offer core financial services without applying for a full banking license from day one. This structure is used globally and allows neobanks to focus on user experience, product innovation, and digital operations.
Even when partnering with a licensed entity, neobanks still share certain compliance duties. These often include:
- KYC/AML checks to verify customer identity and monitor for suspicious activities
- Data protection and cybersecurity standards
- Ongoing reporting depending on the region or product offered
- Adhering to local and cross-border financial regulations
In many cases, BaaS providers or sponsor banks manage the most complex regulatory processes, while the neobank ensures that its onboarding flow, customer operations, and internal policies meet the required standards.
This collaborative model creates a balance. The licensed bank ensures regulatory oversight and financial safety, the neobank delivers a seamless digital experience, and the BaaS provider connects both sides through scalable technology and compliance workflows.
As a result, neobanks can operate safely within legal frameworks while still innovating rapidly in the digital finance space.
Card issuing, partnering & settlement flows
A key example of this partnership model in action is card issuing – a feature that looks simple to users but involves intricate backend processes.
Most neobanks don’t issue cards entirely on their own. They partner with card networks (like Visa or Mastercard) and licensed issuers through BIN sponsorships. This lets them create branded debit or credit cards without holding a full banking license.
Modern card issuing runs through API integrations with third-party providers, covering everything from virtual and physical card creation to tokenization for secure digital payments.
Behind every transaction, neobanks rely on automated settlement and reconciliation systems to match payments, ensure ledger accuracy, and finalize fund transfers between parties.
For example, in international transfers, a neobank may route payments through correspondent banks and FX rails (like SWIFT or Wise) to complete currency conversion and settlement These processes run automatically via APIs, reducing manual errors and enabling real-time financial reporting.
What do they offer?
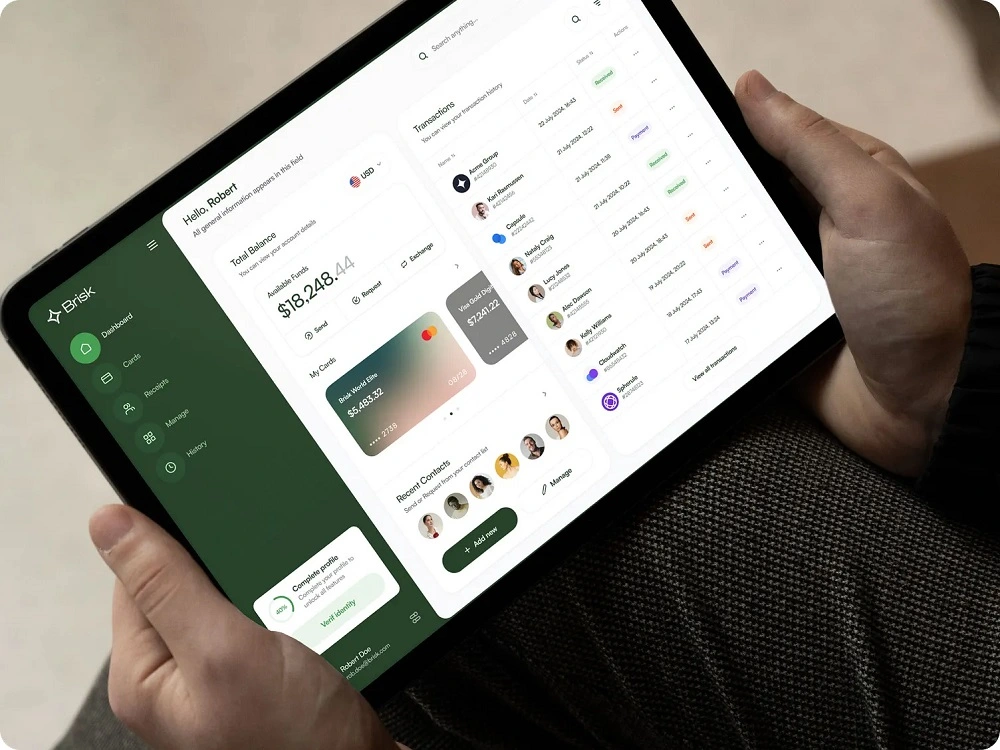
All these technical components and partnerships ultimately serve one goal, to deliver seamless banking experiences to users. It provides specialized financial products, such as:
- High-interest checking and savings accounts.
- Credit and debit cards for real-time transactions.
- Easy, low-cost international transfers and FX services.
- Financial management tools (budgeting, spending insights, automated savings features, etc.)
If you’re exploring neobanking or want to discuss how they work in practice, feel free to reach out. We’re always open to sharing insights and helping you navigate the landscape.
How do neobanks make money?
Now you know neobank offers all these benefits for users. But how do they actually make money?
Unlike traditional banks, neobanks don’t charge account maintenance fees. Instead, they generate revenue through various channels:
- Interchange fees: Every time you pay with a debit or credit card, neobanks earn 1-2% from transaction fees. The more transactions, the higher their revenue.
- Subscription plans: Offer free and premium accounts with perks like investment tools, cashback rewards, and exclusive benefits.
- Lending & interest on loans: Charge fees on currency exchange, international transfers, and crypto transactions, profiting from high trading volumes.
- Foreign exchange and crypto trading fees: Apply fees to currency exchanges and international transfers along with crypto transactions at a low exchange rate while generating revenue through frequent transactions.
- Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS): Partner with fintech startups to provide financial services via API, earning fees for integrations and service usage.
- Partnerships & affiliate marketing: Collaborate with insurers, investment platforms, and fintech firms to earn commissions from referrals and in-app financial tools like wealth management and stock trading.
However, profitability remains a key challenge for most neobanks. Their unit economics depend on balancing three critical factors:
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Often high due to marketing and referral incentives.
- Lifetime Value (LTV): Driven by retention and successful cross-selling.
- Interchange Margins: Under pressure as regulations and network fees tighten.
To stay profitable, modern neobanks are focusing on monetizing value-added services (wealth management, credit lines, B2B payments) and improving cost-to-income ratios through automation and partnerships with BaaS providers.
Are neobanks safe?
Neobanks are safe when they adhere to strict financial regulations with strong cybersecurity measures. These will make sure they are sustainable while minimizing risks related to fraud, cyber threats, and financial instability.
- To remain compliant and protect deposits, most neobanks either partner with licensed banks or obtain their own banking licenses.
- To protect user data, neobanks utilize encryption, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and biometric login, while AI-powered fraud detection manages transactions, detects suspicious activities to avoid.
- To identify cyber threats and data breaches, neobanks conduct regular penetration testing, red team exercises, and incident response planning. However, this practice can involve a third party like a cybersecurity outsourcing service provider.
- To protect customer deposits, many neobanks hold FDIC (or equivalent) deposit insurance up to a certain limit. At the same time, they require customers to verify deposit protection policies before entrusting large sums.
Neobank regulation and compliance
While cybersecurity keeps data safe, compliance is the foundation of user trust.
Failure to meet the regulatory requirements or noncompliance can cause neobanks to suffer from heavy fines – such as the £7.6 million penalty imposed by the UK’s FCA in 2022, license revocation, operational restrictions on customer acquisitions and transactions, and even legal action against executives for financial misconduct.

Key regulatory issues
- Approval and licensing from national financial authorities (FCA, MAS, OCC, etc.)
- Compliance with Anti-money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC).
- Adherence to data protection and privacy laws (GDPR, PSD2, or regional equivalents)
- Capital adequacy and risk management requirements for licensed entities
- Ongoing transaction monitoring and suspicious activity reporting
Regional regulations
Neobank regulations differ by region.
In the U.S., most partner with FDIC-insured banks to protect deposits up to $250,000 and comply with agencies like the OCC and CFPB. The U.K. enforces full licensing under the FCA and PRA, with FSCS coverage up to £85,000 and strong support for open banking. Across the EU, PSD2 regulations mandate secure API access, driving interoperability between banks and fintechs.
In Asia, markets like Singapore and India promote innovation through regulatory sandboxes by MAS and RBI, while Japan and Hong Kong apply similar frameworks under tight data and cybersecurity rules, which ensure consumer protection while encouraging fintech growth.
Emerging trends
Several emerging trends are shaping the neobank landscape today. These shifts reflect how customer expectations, technology, and financial ecosystems are evolving, and they highlight where new opportunities are opening in the market.
AI-Driven personalization.
AI is becoming central to how neobanks improve customer experience. Modern neobanks use machine learning to analyze spending patterns, predict financial needs, and deliver more personalized budgeting tools or recommendations. By 2025, ~70% of neobanks plan to use predictive analytics for credit scoring and personalization. This trend shows a broader shift toward smarter, context-aware banking experiences rather than generic digital interfaces.
Embedded finance & open banking.
Embedded finance continues to grow as companies outside the financial sector (such as retail, logistics) and SaaS platforms are integrating banking features directly into their products. By 2025, 80% of neobanks are building APIs that let any business from ride-sharing apps to online stores add banking features directly into their platforms. This creates opportunities for neobanks to become infrastructure providers or collaborate with non-bank brands to power payments, lending, or account services behind the scenes.
Rise of B2B and vertical neobanks
More neobanks are focusing on specific business niches instead of serving mass consumers. Nearly 30% of new neobank accounts in 2024 were for small businesses, freelancers, or startups operating in highly regulated sectors. This trend reflects market demand for tailored financial services rather than broad, one-size-fits-all digital banks.
Stronger focus on compliance and resilience
As the industry matures, regulators worldwide are tightening requirements around KYC, capital, risk monitoring, and data governance. Neobanks responding to this trend are investing in risk management and transparency, aiming to build long-term stability and trust.
Conclusion
Neobanks continue to reshape modern banking by offering digital-only services that are faster, more transparent, and more aligned with how people manage money today. For startups and businesses, this shift opens the door to new models that can deliver better customer experiences without the limitations of traditional infrastructure.
As we move into 2026, the focus is no longer about competing with incumbents or chasing user numbers. What truly matters is building trust through compliance, operational resilience, and technology that solves real customer problems. Neobanks that stay grounded in these principles will be the ones that grow sustainably in the years ahead.
Recommended reading on Neobanking:
- White-label neobank: comparison, costs & how to choose in 2026
- Top 10 ready-made neobanks for business – smart, but enough?
- How to start a Neobank app in 6 easy steps
- 10 best Neobank app development companies to watch in 2026
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating / 5. Vote count:
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.




