In this article by Synodus, let’s delve deeply into details about customer analytics in retail, its significance with key features, and several best practices of customer behavior analysis.
What is customer analytics?
Customer analytics is the process of collecting customer behavior data with the aim of analyzing their actions and motivations. To be more specific, with both refined and raw data, we can come up with many details about the stores that customers visit, the reasons for going there, the items they purchase, and the variables that affect those purchases.
Customer analytics uncover new sales and marketing potential by providing a complete picture of the retail scene and much insights into the perspective of the customer.
Why is customer analytics important to your retail business?
Far-reaching effects on profits and revenues

Companies from all over the world and in all industrial sectors are approaching their businesses with a focus on the customer to gather enormous amounts of consumer journey because these informative data have huge impacts on the retail profits and revenues.
So you can determine which product and client kinds are the most valuable if you know who purchased what and through which channels. Then by perfecting the customer journey, you may find out other potential customers and better boosting ways to increase purchase and loyalty.
Let’s examine the three key pillars of retail success are influenced by customer analytics below.
- Customer Acquisition: By optimizing marketing expenditure through deeper consumer insights, analytics may reduce the cost of client acquisition. Marketing may target and acquire clients with characteristics that are similar to those of your top customers by using behavior analytics. Such prospects will have a high lifetime value and a better likelihood of responding favorably to your communications and incentives.
- Customer Engagement: Analytics may reveal the format and genre of information that appeals to your target audience. These data not only assists you in providing the appropriate content but also in spotting possibilities for up-sells, cross-sells, and next-best offers. By assisting marketers in developing targeted offers based on client behavior profiles, it can increase buy rates.
Customer Retention: Customer turnover may be anticipated based on trends in customer behavior. Marketing can be informed about clients who appear ready to go and provided information on what incentives could work best to keep them. Marketers might then devise a next-best retention offer as a last-ditch effort to keep the client. Beyond retention, behavioral insights may be leveraged to create brand-loyalty-promoting loyalty programs.
Beneficial influences on operation and demand forecast
Every retailer should be aware that rising profits do not always result from rising customer spending. At the same time, it also occurs from a well-run company, which minimizes investment in labor and inventory while eliminating wasteful spending.
Vendors may better target their marketing budgets to reach customers at the correct time and manage the supply chain when handling the operation. They understand how to design workforce schedules to give appropriate customer help during peak periods of business. These customer journey analytics can also support retailers on how to plan stocking activities to match purchasing requests.
Moreover, gathering and analyzing customer data from a variety of sources can bring up better understanding of their behavior, preferences, feedback, and satisfaction. By using historical patterns, sales data may be used to assess performance in the past and present and forecast demand in the future.
Which types of customer data is the most vital to business?
We’ve seen how crucial customer analytics are to the retail sector, but before performing research, it’s a good idea to select the suitable strategy to collect data and the kinds of datasets you’ll require to support your business choices. It can be a mix of various factors. Below are four data kinds that frequently contribute to data analytics to aid in your decision-making.
Descriptive data
In many ways, descriptive data is a detailed form of identification because it turns many types of acts into data points. It covers usage rates, website visits, email opens, and purchasing trends. Point-of-sale data may be the most significant source of descriptive data in the retail industry.
For current persona-based marketing, which compiles data from all of your customers into a single customer profile from which you can develop a business strategy, gathering descriptive data is a crucial component.
Identity data
Identity data may be the most fundamental, containing details like a person’s name, gender, contact information, email address, and social network accounts. These informational pieces confirm that the people being contacted are current clients who are approved to do so.
Identification resolution, which refers to the process of establishing a person’s identification, has emerged as a significant trend in recent years. Many businesses are turning to technology to better target their customers and use their data to build more complete portraits of their identities.
Behavioral data
Behavioral data focuses on the actions and behaviors of customers. It can show trends in the topics like how frequently customers visit a certain store, how frequently they come in person as opposed to online, which pages of a website they view, how much money they spend, etc. To further help explain the behavioral datasets, it is also possible to ask customers about the motivations behind their actions or their opinions of the businesses they visit.

Consumer trackers, which are frequently employed in retail environments, can be crucial for gathering information on end users’ preferences for brands. These methods can be automated more thoroughly online, for instance by tracking which links people click or how far they scroll (a well-known use case for Google Analytics). When taken as a whole, these data can provide more general insights that help enhance the online purchasing experience.
In order for organizations to capitalize on data-driven trends, behavioral data tries to extract various lessons from such patterns.
Qualitative data
Qualitative data represents what consumers think, whereas identity and descriptive data represent who consumers are and what they do. In qualitative research, the quality of the responses is the main concern rather than the volume of data gathered.
Through oral dialogues, focus groups, video survey replies, or anthropological observations, it offers an in-depth look into consumer opinions. Retail firms find it simple to visualize the ideas and motives driving their customer journey thanks to the anecdotal evidence of qualitative consumer behavior.
Normally, an audience sample that is typical of the client’s target market is used to collect qualitative data. Because the sample size is lower than in quantitative research, a deeper understanding of consumer behavior is possible rather than a broader one.
Moreover, interviews are conducted with individuals or groups of individuals regarding the subject is more preferred, and general rather than specific questions are used, providing respondents with merely a topic to discuss rather than a yes/no question.
6 Types of customer analytics and how to use them
A customer analytics is a method of keeping track of consumer behavior and here are six different kinds of consumer analytics you may use in your company.
Segmentation analytics
Most likely, numerous groups with varied interests make up your consumer base. It makes no sense to market to these people in the same way. You can understand each group better and tailor your messaging, content, and assistance by segmenting your audience.
Additionally, segmentation analytics aids businesses in identifying emerging client clusters and comprehending the motives and actions of such customers. Teams may increase customer satisfaction and retention KPIs by using segmentation data to discover new methods to connect with and interact with each category of your audience.
Customer acquisition analytics
Any firm must have a strategy for acquiring new clients but it is not always easy to carry out. Customer acquisition efforts may be expensive, and it can be difficult to determine whether the upcoming clients are actually a suitable fit for your goods or services. Analytics on customer acquisition show how successful your acquisition plan is.
Analyzing client acquisition data will allow you to determine your cost per lead and work to cut it down. The amount of qualified leads generated by several ad campaigns may also be compared, to see which one is more effective. Combining customer engagement analytics with customer acquisition analytics can also reveal areas where personalisation might be enhanced and your go-to-market plan could be improved.
Customer churn analytics
Analytics on customer churn reveal the average length of a customer’s association with a business. Customers that cancel subscriptions, return goods, or stop making new purchases are said to have a high rate of churn. Customer churn metrics are highly scrutinized by businesses due to their huge financial impact.
Maintaining a check on churn is an important task for every department, so it will be more carefully controlled when erratic changes happen.
Usually, the rising turnover rates often signify problems with the product or customer service. Early detection of these issues allows businesses to take swift corrective action, addressing the underlying reason of churn and brainstorming potential new customer loyalty programs, price adjustments, and customer service policy revisions. Companies can identify what is doing effectively to increase retention when customer churn data are low.
Customer engagement analytics
It is obvious that customers engage with brands in a variety of ways, such as via using various goods and services, utilizing social media, clicking on advertisements, reading email newsletters, and answering NPS surveys.
So the customer engagement analytics evaluates the intensity of the relationship, showing the most effective marketing strategies, the difficulties clients are having utilizing your products, and how they feel your services may be improved. The marketing, product, sales, and even customer success departments may all greatly benefit from this input.
Additionally, outlining the whole customer journey may provide businesses suggestions for where to simplify the experience and where to add more customized touches.
Customer lifetime value analytics
You should know that not all consumers make further purchases. Some buyers will try out your goods or service once and never purchase it again. Others buy something each week. The secret to financial success is understanding the differences.
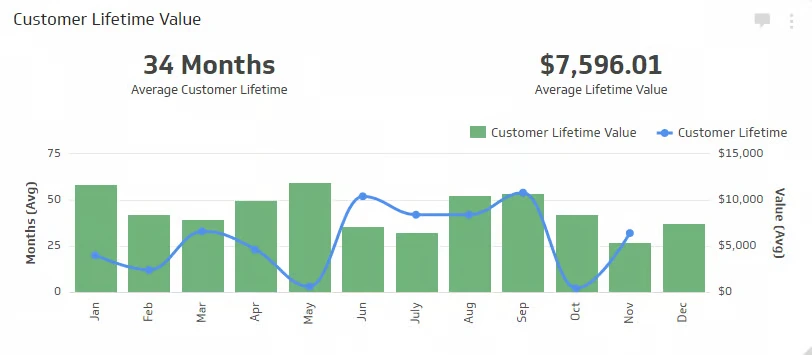
The consumer lifetime value analytics reveals how much the typical consumer spends over the course of their relationship with your brand (lifetime). In other words, customer lifetime value analytics show which customer kinds are the most cost-effective for you.
Data analytics of customer lifetime value enable you to target the correct customers with your acquisition, remarketing, and retention efforts, allowing you to spend money more wisely and increase earnings more quickly.
Customer satisfaction analytics
You definitely can find the customer satisfaction breadcrumbs everywhere: on social media, customer support surveys, in-app polls, etc. Analyzing customer happiness aims to quantify and improve consumers’ perceived value and, as a result, brand loyalty.
Of course, analytics on customer satisfaction combine qualitative and quantitative techniques to get a comprehensive picture of how customers see your goods or services. Companies should constantly keep an eye on customer satisfaction numbers, but also should pay particular attention when introducing new services or goods, changing their branding significantly, or modifying their support system.
Best practices for customer behavior analysis
A consumer behavior analytics must include the following practices to provide the most genuine and precise insights:
- Take advantage of interaction data from both digital and physical touchpoints, as well as all channels.
- Investigate real behavioral data at the individual level to uncover information that may be obscured in aggregated data.
- Consider the factors that influence and the ways in which consumers switch between segments over time to build a more realistic picture of the customer lifecycle.
Customer behavior analytics enables merchants to draw insightful conclusions from their customer data, enabling them to outperform their rivals in terms of customer wallet share.
- Suggested for you: 9 Representative Retail Data Analytics Use Cases & Examples
Wrapping up
Customer analytics in retail is now indispensable for any business operating in retail sector. By reaching the right people with highly relevant offers and communications, businesses may improve response rates, client loyalty, and ultimately ROI through careful data analysis. And by focusing on the customers most likely to respond to a campaign, businesses may cut marketing expenses. And there are still much more benefits, as mentioned above.
If you would love to give customer analytics a try, but do not know where to start, do not hesitate to reach out to our experts! We would love to consult you with the best solution for your business’s needs and struggles.
More related posts from Big data blog you shouldn’t skip:
- Detailed Customer Feedback Analysis Guide 2025
- Exploring Data Analysis Case Study: Use Cases Across 8 Diverse Industries
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating / 5. Vote count:
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.




